
The Invisible Polluter: Why Digital Carbon Footprint Matters
If the Internet were a country, it would be the fourth largest polluter in the world, ranking just behind the United States, China, and India.
For years, corporate sustainability (ESG) strategies have focused on physical waste: plastic reduction, electric fleets, and supply chain logistics. While necessary, these efforts ignore a growing, invisible giant. The global digital ecosystem—spanning data centers, transmission networks, and end-user devices—now accounts for approximately 3.7% of global greenhouse emissions, surpassing the entire aviation industry.
At The Greenwise Agency, we argue that the next frontier of corporate responsibility is not just physical; it is computational.
Key Finding: An average corporate website produces 1.76g of CO2 per page view. For a site with 100k monthly views, that is 2,112kg of CO2 per year—equivalent to driving a petrol car for 10,000km.
The Anatomy of “Digital Bloat”
Every interaction on a screen triggers a chain reaction of energy consumption. Data centers must be cooled, routers must transmit signals, and CPUs must process scripts. The problem isn’t the usage; it’s the inefficiency.
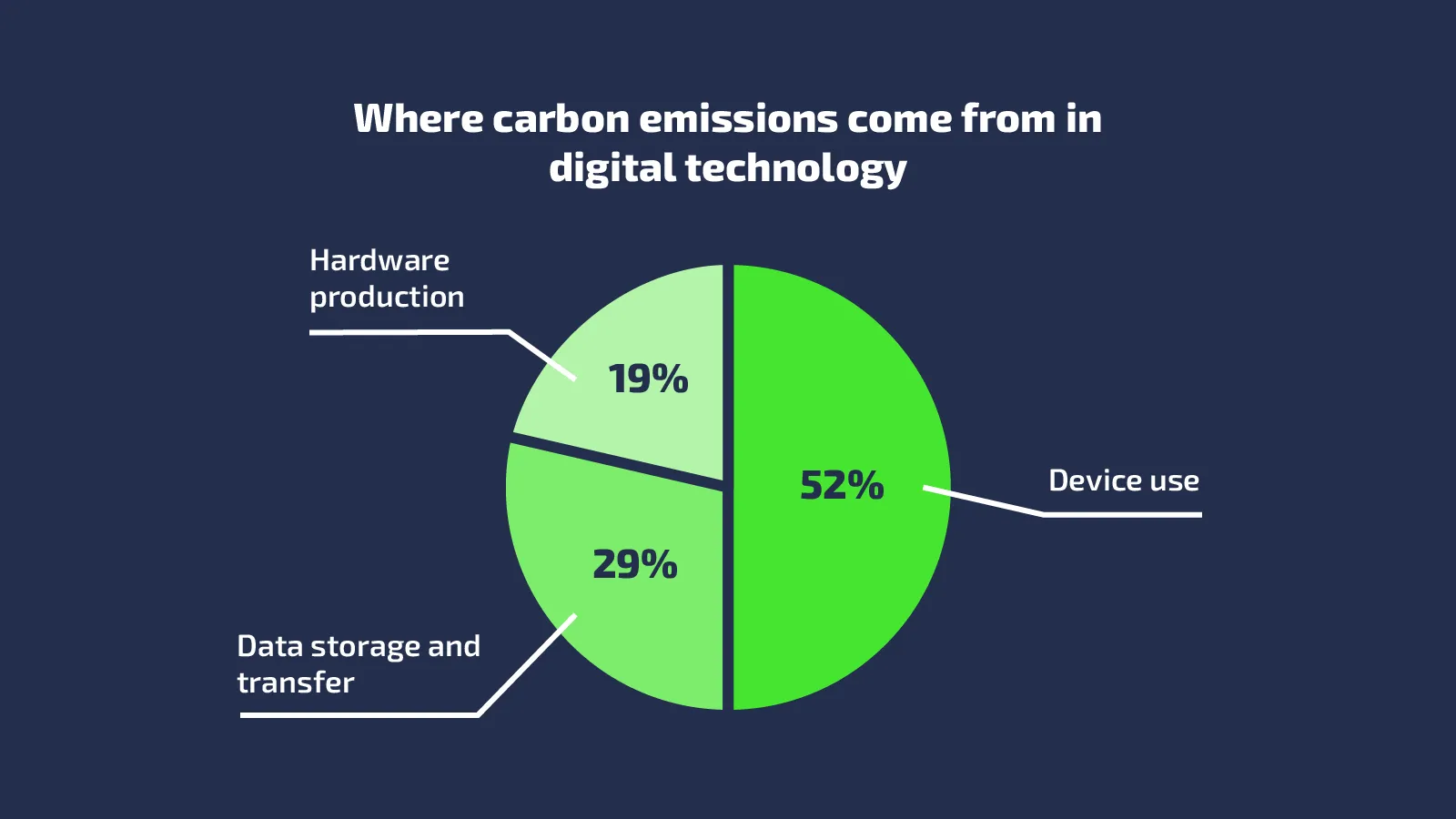 Figure 1: The breakdown of carbon emissions in digital technology (Source: The Greenwise Agency Internal Research, 2025).
Figure 1: The breakdown of carbon emissions in digital technology (Source: The Greenwise Agency Internal Research, 2025).
Over the last decade, the average web page size has increased by 300%, yet the information density remains largely unchanged. We are transmitting:
- Heavier Libraries: Unused JavaScript bundles blocking the main thread.
- Uncompressed Assets: High-resolution images serving 4K pixels to mobile screens.
- Redundant Scripts: Third-party trackers executing in the background, draining battery life.
The Business Case for Digital Decarbonization
Beyond the environmental imperative, reducing digital waste is a superior business strategy. The correlation is direct: Sustainable code is performant code.
- Lower Latency: Optimized assets load faster, directly improving Core Web Vitals and SEO rankings.
- Reduced Hosting Costs: Lighter applications require less processing power (CPU) and storage, lowering cloud infrastructure bills.
- Regulatory Compliance: With the new EU CSRD (Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive), companies must report on their Scope 3 emissions—which now include their digital supply chain.
Our Methodology: The Zero-Waste Stack
We founded The Greenwise Agency to engineer solutions for this specific problem. We are moving beyond the “Agency” model into an “Infrastructure Partner” role. Our 2025-2026 roadmap targets the three layers of digital interaction:
1. The Physical Layer (Focus One)
Replacing disposable paper networking with reusable NFC technology. A single Focus One card replaces ~2,000 paper cards in its lifecycle, eliminating ink, bleach, and transport logistics.
2. The Logic Layer (CodeGreen)
We don’t just “build webs”; we audit them. Our proprietary algorithm refactors corporate web architecture to minimize energy intensity per session.
3. The Human Layer (Impact Academy)
Technology is only as green as the people using it. Our Fundae-subsidized training bridges the gap, teaching teams to manage cloud resources responsibly.
The transition to a net-zero economy requires more than planting trees. It requires rewriting the code that powers our world.
Welcome to the era of Sustainable Digital Infrastructure.